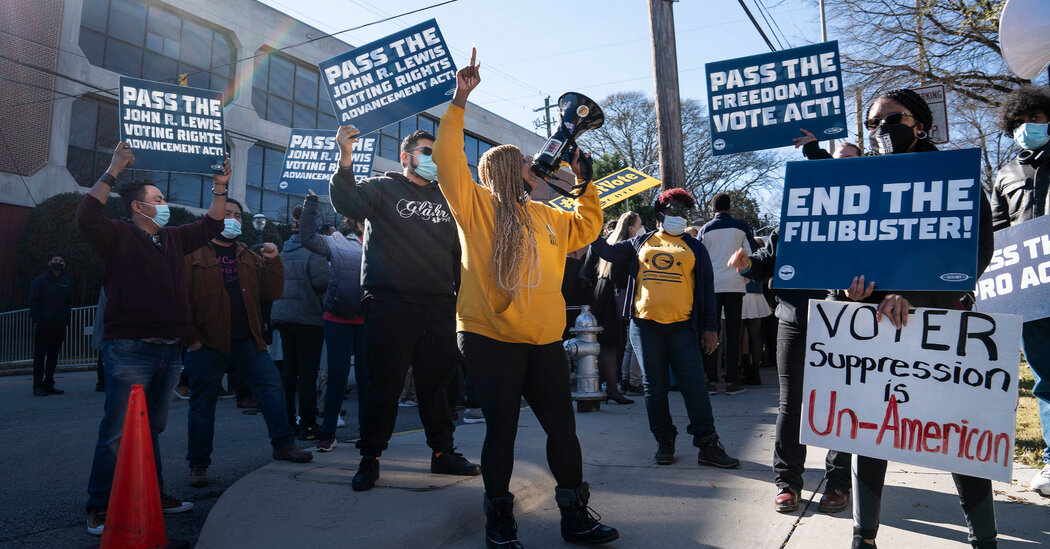
With their broad voting rights push nearing a dead end, Democrats must soon decide whether to embrace a far narrower bipartisan effort to protect vote counting and administration.
WASHINGTON — With their drive to secure far-reaching voting rights legislation nearing a dead end, Senate Democrats face a decision they had hoped to avoid: Should they embrace a much narrower, bipartisan effort to safeguard the vote-counting process, or continue what increasingly looks like a doomed push to protect access to the ballot box?
A growing group of Senate Republicans and centrist Democrats is working on legislation to overhaul the Electoral Count Act, the 19th-century law that former President Donald J. Trump sought to exploit to overturn the 2020 presidential election. That effort is expanding to include other measures aimed at preventing interference in election administration, such as barring the removal of nonpartisan election officials without cause and creating federal penalties for the harassment or intimidation of election officials.
Democratic leaders say they regard the effort as a trap — or at least a diversion from the central issue of voter suppression that their legislation aims to address. They argue that the narrower measures are woefully inadequate given that Republicans have enacted a wave of voting restrictions in states around the country that are geared toward disenfranchising Democratic voters, particularly people of color.
Still, even if there is no consensus to be found on a bill addressing how votes are cast, proponents say there is a growing sentiment in favor of ensuring that those that are cast are fairly counted.
“There is a lot of interest, a lot of interest,” said Senator Susan Collins, Republican of Maine, who is leading one effort with Senators Kyrsten Sinema of Arizona and Joe Manchin III of West Virginia, both centrist Democrats, and Senators Mitt Romney of Utah, Thom Tillis of North Carolina, Roger Wicker of Mississippi and Joni Ernst of Iowa, all Republicans.
Senator Jeanne Shaheen, Democrat of New Hampshire, also listened in on a call on the matter this month but remains noncommittal.
“I’m not saying this is going to be easy,” Ms. Collins added, “but I’m optimistic.”
A separate group — including two Democratic senators, Richard J. Durbin of Illinois and Amy Klobuchar of Minnesota, and Senator Angus King, a left-of-center independent from Maine — is looking at changing how Congress formalizes the election results to head off another attempt like the one Mr. Trump made to have allies on Capitol Hill try to toss out state electoral votes.
But most Democrats are reluctant even to discuss the matter until after the far more comprehensive voting rights bill they call the Freedom to Vote Act is put to rest next week, a near certainty after Ms. Sinema and Mr. Manchin said this week that they would not vote to change Senate rules on the filibuster to enable their party to push it through unilaterally.
“There are two issues going on right now in the country. One is voter suppression — these subtle laws that make it harder for people to vote,” Mr. King said. “The other piece is voting administration, where you get into substituting partisan people for nonpartisan administrators, purging voter election boards, allowing election boards to eliminate polling places and also the whole mechanics of counting.”
He added, “There’s a reasonable opportunity here for a bipartisan bill, but my concern is that it will be viewed as a substitute for the Freedom to Vote Act, and that’s just not the case.”
Members of both parties are concerned about the counting and certification of ballots after they have been cast. President Biden was emphatic on the point when he emerged Thursday from a fruitless lunch with Senate Democrats, pleading with them to change the filibuster rules around voting.
“The state legislative bodies continue to change the law not as to who can vote, but who gets to count the vote, count the vote, count the vote,” he said, his voice rising in anger. “It’s about election subversion.”
And some academic experts say protecting election administration and vote counting, at this moment, is actually more critical than battling restrictions on early and absentee voting and ballot drop boxes.
“I’ve been saying this for the last year: The No. 1 priority should be ensuring we have a fair vote count,” said Richard L. Hasen, a law professor at the University of California, Irvine, who has drafted his own prescriptions for safeguarding elections after Election Day. “We are in a new level of crisis. I never expected in the contemporary United States that we would have to have legislation around a fair vote count, but we have to have it now.”
Senator Mitch McConnell of Kentucky, the Republican leader, has opened the door a crack to changing the Electoral Count Act, which Mr. Trump and his legal advisers speciously claimed gave the vice president the power to unilaterally reject the electors from states deemed contested.
“It obviously has some flaws. And I think it should be discussed,” Mr. McConnell told reporters on Tuesday. “That is a totally separate issue from what they’re peddling on the Democratic side.”
Democrats are leery. They fear Republicans want to reassure Mr. Manchin and Ms. Sinema that if, as promised, they reject their party’s efforts to do away with the filibuster to pass voting rights legislation, they will have the bipartisan alternative they crave.
Senator Chuck Schumer of New York, the majority leader, has said not only would that alternative be wholly insufficient, but it also would probably not materialize.
In 2019, as Democrats were pushing for gun safety legislation after a pair of mass shootings, Republican leaders who opposed the bill raised the prospect of narrower legislation to help law enforcement take guns from those who pose an imminent danger. Once the Democratic bills failed, the more modest one did, too.
Understand the Battle Over U.S. Voting Rights
Why are voting rights an issue now? In 2020, as a result of the pandemic, millions embraced voting early in person or by mail, especially among Democrats. Spurred on by Donald Trump’s false claims about mail ballots in hopes of overturning the election, the G.O.P. has pursued a host of new voting restrictions.
“Is it something that we might consider? Yes,” Mr. Schumer said of vote counting legislation, “but not as a substitute for these vital, vital provisions which will keep the right to vote and prevent voter suppression.”
The lawmakers who are eyeing an overhaul of the Electoral Count Act say they want to address what happened last year, when allies of Mr. Trump challenged the election results during a Jan. 6 joint session of Congress, and the president was pressuring Vice President Mike Pence, who presided over the session, to reject the disputed electors.
One proposed change would make clear that the vice president has only a ceremonial and administrative role in the counting of electoral votes. Another would make it far more difficult to raise objections under the law, which currently allows a single senator and House member to mount a challenge to a state’s electoral votes. In the bill drafted by Mr. King, Mr. Durbin and Ms. Klobuchar, electors could be challenged only if a third of each chamber objected.
In the House, four members of the committee investigating the Jan. 6 attack — Representative Liz Cheney, Republican of Wyoming, and Representatives Zoe Lofgren and Adam B. Schiff of California and Jamie Raskin of Maryland, all Democrats — are also working on a rewrite of the Electoral Count Act. They have also discussed whether to expand their bill to include measures blocking anti-democratic election practices at the state level, such as allowing partisan legislators to select presidential electors instead of the voters.
Ms. Collins’s group has discussed several measures, such as expanding the allowable uses of federal election grants, now mainly for buying voting machines not connected to the internet, to include recruiting and training election workers, purchasing voting machines that create paper ballots and expanding cybersecurity efforts. She said the group also agreed that stiff new penalties should be created to thwart the kind of harassment and intimidation of election officials that supporters of Mr. Trump had meted out, a provision taken from the Freedom to Vote Act.
They are still debating how far to go in blocking the removal of nonpartisan election officials without cause by partisan state officials or legislators. The Democrats’ voting rights bill makes such actions a federal crime unless malfeasance by the election official can be proved.
For Democrats, that provision is a necessity. And they say for Ms. Collins’s measure to gain any traction, Republicans would have to accept some provisions from the voting rights bill to combat voter suppression, such as a minimal number of early voting days or a compromise provision drafted by Mr. Manchin that accepts voter identification laws but ensures that an array of identifications would be acceptable.
“It’s very important to ensure that the votes are counted both with provisions in the Freedom to Vote Act and the Electoral Count Act, but that’s still no substitute for protecting people’s right to vote from the beginning,” said Ms. Klobuchar, who is chairwoman of the Rules Committee, which would consider such legislation.
Ms. Collins said her group — which includes two additional Republicans and two additional Democrats who have not publicly divulged their involvement — will meet again the week after the voting rights bill is blocked.
“It’s evident we have to get through this stage,” she said.
But, she added, she is not seeking Mr. McConnell’s blessing. Earlier this month, she said she spoke at a closed-door luncheon of Republican senators to walk her colleagues through the effort. Mr. Romney stood to back her up.
“We don’t feel like we have to ask for permission,” she said.
Luke Broadwater contributed reporting.